

The liver facilitates several bodily functions- after all it is the largest internal organ in the body. It metabolises nutrients, detoxifies harmful substances, and produces bile, a yellow-green fluid that aids digestion. Most importantly, it stores vitamins, regulates blood sugar, and contributes to immune function.
A fatty liver disease primarily affects the liver by causing an accumulation of fat within liver cells. This can lead to many complications including painful symptoms in your legs. Speaking with the OnlyMyHealth team, Dr Sharath Kumar, JG Surgical Gastroenterology, Apollo Clinic, Koramangala, explains how and signs to watch out for.
Also Read: Excessive Alcohol Consumption Can Contribute To Stroke Risk: Step-By-Step Strategies To Stop Drinking
Fatty Liver Disease Prevalence
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, occurs when excess fat builds up in the liver, meaning when fat reaches 5-10% of the liver’s weight. There are two main types of fatty liver disease including:
Alcohol-induced fatty liver disease (AFLD): It is caused by regular alcohol consumption. Alcoholic Liver Disease (ALD) accounts for 4% of mortality and 5% of Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) with Europe being the worst affected, says a study published in the Journal of Hepatology, adding, “In 2010, almost half a million deaths were attributable to alcohol related cirrhosis.”
Non-Alcohol Related Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): This type of fatty liver disease is not related to alcohol consumption, but had a global prevalence of 38% between 2016-2019; previously it was 25.3% in 1990-2006. Up until now, researchers haven’t found the exact cause of the condition.
How Does Fatty Liver Disease Affect Your Legs
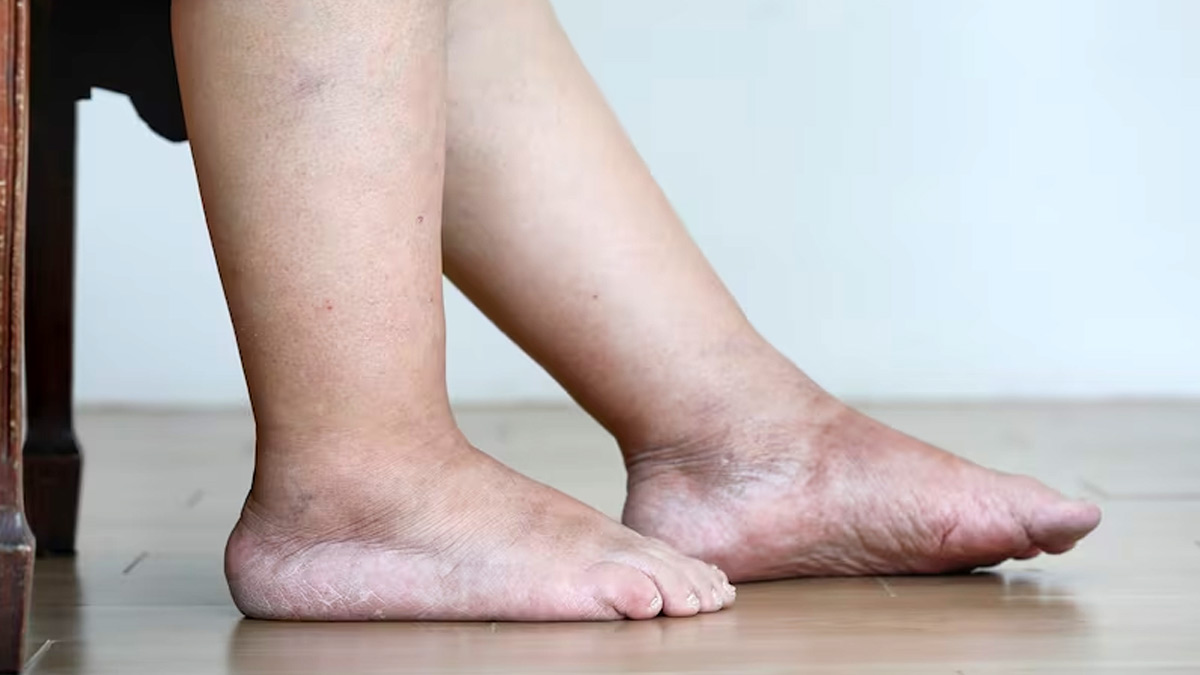
Fatty liver disease does not directly impact the legs, rather progresses to more severe stages, such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) or cirrhosis, which can lead to systemic effects or problems with the circulatory system that affects the whole body, including the legs.
Individuals suffering with NASH and those who have experienced considerable liver damage, may experience ‘swelling in the legs’, also called oedema, and ‘fluid accumulation in the abdomen’, called ascites, according to Cleveland Clinic.
Cedar Sinai explains that it occurs because of the increased pressure in the vein that moves blood through your liver, known as the portal vein.
In addition, Dr Kumar suggests an association between fatty liver disease and insulin resistance (type 2 diabetes). He says, “Diabetes can lead to circulatory problems and nerve damage, especially in the lower extremities. This can result in poor blood flow, decreased sensation, and slower wound healing, increasing the risk of foot ulcers and infections.”
“Fatty liver disease is also a risk factor for Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs). Poor circulation resulting from heart conditions can lead to Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), a condition that reduces blood flow to the legs and feet,” the doctor adds.
According to the doctor, this can cause pain, cramping, and weakness in the lower extremities during physical activity.
Other Symptoms To Watch Out For
Here are the symptoms of fatty liver disease:
- Fatigue
- Abdominal discomfort or pain
- Unexplained weight loss
- Jaundice – yellowing of the skin and eyes
- Elevated liver enzymes in blood tests
- Dark urine
- Pale-coloured stool
- Loss of appetite
- Weakness
- Confusion in severe cases
- Red palms in advanced stages
- Spider-like blood vessels on the skin
How To Prevent A Fatty Liver Disease
“Preventing fatty liver disease involves adopting a healthy lifestyle and making choices that support liver health,” says Dr Kumar.
According to him, obesity is a major risk factor for fatty liver disease, which is why one must aim to achieve and maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity.
The doctor recommends focusing on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. He warns against the consumption of sugary foods, processed foods, and foods high in saturated and trans fats. In addition, limit your intake of refined carbohydrates and added sugars. These can contribute to insulin resistance and the development of fatty liver disease. Therefore, choose complex carbohydrates and foods with a low glycemic index, says the doctor.
Avoid excessive alcohol consumption, which is a known cause of fatty liver disease. If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation. For most adults, this means up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men, as per the doctor’s recommendation.
Lastly, engage in regular physical activity, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
Pro-Tip
“If you have diabetes or insulin resistance, work closely with your healthcare provider to manage your blood sugar levels effectively. Proper management can reduce the risk of fatty liver disease.
Certain medications and supplements can impact liver health, which is why consult your healthcare provider before taking any new medications or supplements,” Dr Kumar shares.
اكتشاف المزيد من ينبوع المعرفة
اشترك للحصول على أحدث التدوينات المرسلة إلى بريدك الإلكتروني.
