Urinary Infections In Older Adults: Expert Explains Symptoms and Care Considerations
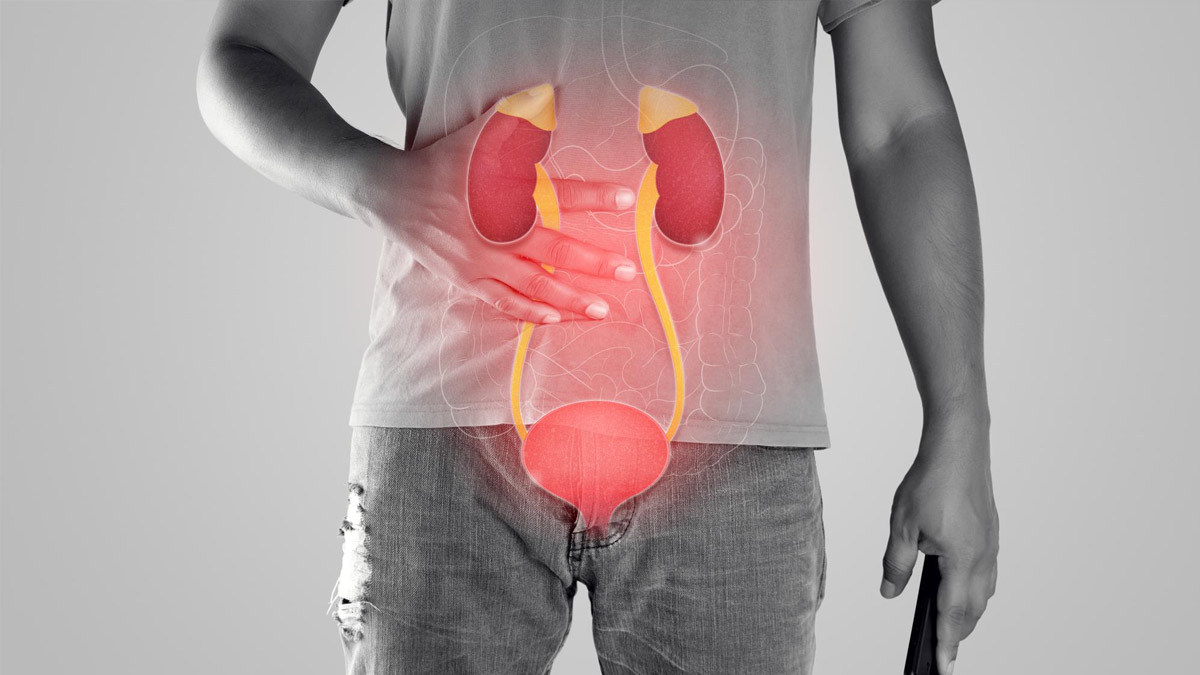

A urinary tract infection (UTI) is a bacterial infection of the urinary tract, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common infection in older adults. UTIs can be more serious in older adults than in younger people and can lead to complications such as sepsis, kidney damage, and even death.
Speaking to the editorial team of Onlymyhealth, Dr. Srivatsan Ramani, Sr. Consultant Urology, Apollo Spectra Hospital, Chennai elucidated the factors that make older adults more susceptible to urinary tract infections, its symptoms and preventive measures. Here is what he shared with us.
Several factors make older adults more susceptible to UTIs, including:
1. Changes in the urinary tract
As people age, the lining of the urinary tract becomes thinner and more fragile, making it more susceptible to infection.
2. Reduced bladder control
Elderly people are more likely to experience incontinence, which can increase the risk of bacteria from the skin or stool entering the urinary tract.
3. Chronic health conditions
Older adults with chronic health conditions, such as diabetes, cancer, and heart disease, are also more likely to develop UTIs.
4. Use of Catheters
People who use indwelling urinary catheters are at a very high risk of developing UTIs as the catheter provides a direct pathway for bacteria to enter the bladder. The bacteria can come from the skin around the urethra, from the patient’s bowels, or the environment.
Also read: Anxiety Management: Manage Anxiety Through 54321 Sensory Method
Symptoms Of UTIs
The symptoms of a UTI in an elderly may be different from those in a younger person. Older adults may not experience the classic symptoms of UTIs, such as burning pain when urinating and frequent urination. Instead, they may experience more vague symptoms, such as fever and fatigue.
Preventive Measures For UTIs
UTIs can be easily treated with antibiotics, but if left untreated, they can lead to serious complications. In addition to antibiotics, several things can be done to help prevent UTIs in older adults. These include:
1. Drinking plenty of fluids
Drinking enough fluids helps to flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
2. Emptying the bladder regularly
Holding in urine for a longer period can increase the risk of infection.
3. Good personal hygiene
This includes washing the genital area with mild soap and water daily.

Also read: Anxiety Management: Manage Anxiety Through 54321 Sensory Method
4. Avoiding constipation
Constipation can put pressure on the bladder and increase the risk of infection.
5. When using a catheter
make sure it is properly cared for which includes cleaning the catheter and changing the bag regularly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, care providers should work closely with elderly people and their families to manage UTIs and prevent complications. This may involve giving information about UTIs, monitoring for symptoms, and ensuring that appropriate treatment is provided. It may also be necessary to involve other medical experts, such as a geriatrician or a nurse practitioner.
