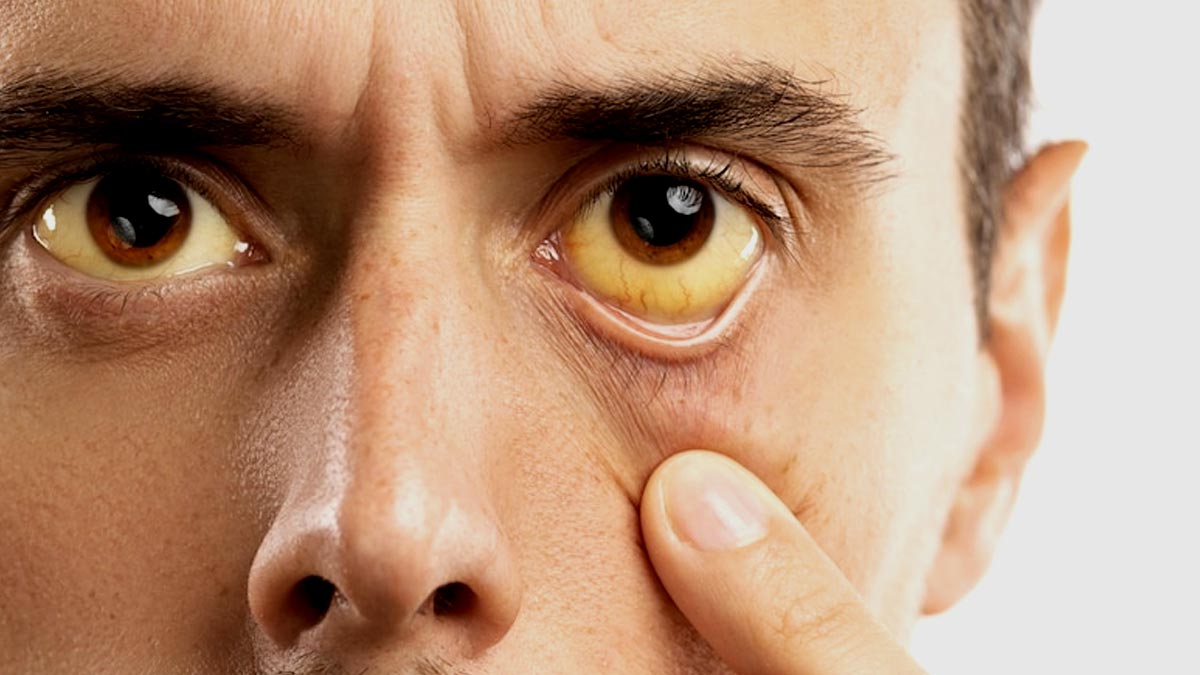

Have you ever looked in the mirror and noticed an unexpected hint of yellow in your skin or the whites of your eyes? This can be an indication of a health condition called jaundice. It is characterised by the increase of bilirubin in the body, leading to the yellowish discolouration of the eyes and urine. It can manifest in various forms, with different underlying causes. We spoke to Dr Rakesh Kumar Jagdish, Consultant Hepatology, Gastroenterology and Liver Transplant Medicine, Metro Hospitals and Heart Institute, Noida Sector 11, Uttar Pradesh, who explained this condition, its signs, causes, and treatment.
What Is Jaundice
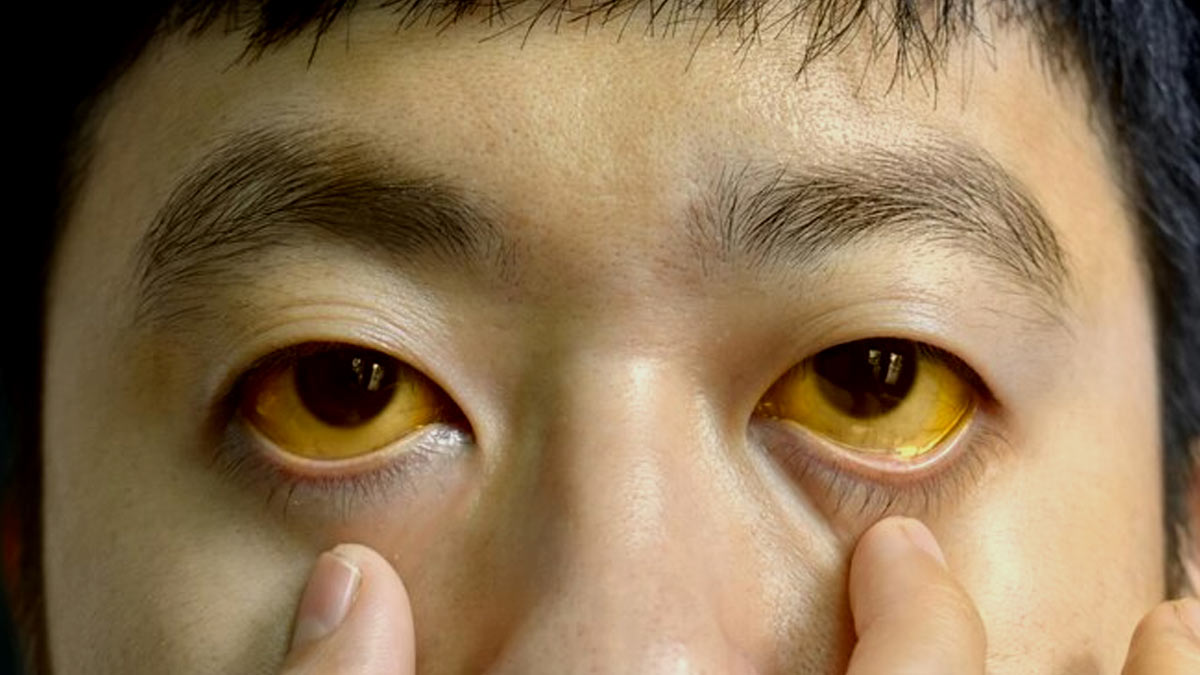
Jaundice, medically known as icterus, is characterised by the yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes. It happens when the bloodstream has an excessive amount of bilirubin, a yellow pigment created during the destruction of red blood cells. Typically, bilirubin is processed by the liver and excreted through the bile. However, when this process is disrupted, bilirubin accumulates in the body, leading to the telltale yellow discolouration.
According to StatPearls, in the first week, jaundice affects about 20% of term newborns, mostly because of an immature hepatic conjugation mechanism. Jaundice in infancy or childhood can also be brought on by congenital abnormalities, excess hemolysis production, poor bilirubin absorption, and poor conjugation.
Also Read: From Swelling To Jaundice: 6 Signs of Fatty Liver Disease Visible On Your Face
Signs of Jaundice
The most prominent sign of jaundice is the yellowing of the skin and eyes. However, there are other subtle indicators to watch for:

- Yellowing: The yellowing usually starts from the face and then spreads to the chest, abdomen, and limbs.
- Pale Stools: Stools might become pale or clay-coloured due to reduced bilirubin excretion.
- Dark Urine: The urine can become dark or tea-coloured as excess bilirubin is eliminated through this route.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Elevated bilirubin levels can lead to fatigue and weakness
- Itching: In some cases, jaundice can cause itching due to the accumulation of bilirubin in the skin.
Types of Jaundice
Jaundice can be classified into different types based on its underlying causes:
Pre-Hepatic Jaundice
Dr Jagdish said, “This type results from haemolysis, a process where red blood cells break down, leading to an increase in bilirubin levels. It does not affect liver enzymes and is often associated with certain types of anaemia.”
Hepatocellular Jaundice
Inflammation or infection of the liver, known as hepatitis, can result in hepatocellular jaundice. Here, bilirubin levels increase along with liver enzyme levels. Several conditions, including alcohol-related hepatitis, viral hepatitis (A, B, C, E), autoimmune hepatitis, drug-induced hepatitis, Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, and more, can lead to this type of jaundice.
Obstructive Jaundice
This form occurs when the bile ducts, which carry bile from the liver to the intestines, become blocked, hampering the flow of bile. Conditions such as Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC), Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC), cholangiocarcinoma, Common Bile Duct (CBD) stones, pancreatic cancer, gallbladder cancer, and periampullary cancer can lead to obstructive jaundice.
Also Read: Understanding Fatty Liver Disease: Expert Lists Swelling and Other Physical Signs
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Management
Dr Jagdish said, “Timely diagnosis and management are vital for treating jaundice effectively. Identifying the underlying cause is the first step, followed by understanding the severity and stage of the disease. Treatment should be tailored according to these factors, taking into account the specific cause, stages, and severity of the condition.”
How To Treat Jaundice

The treatment of jaundice depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition:
- Phototherapy: For newborns with physiological jaundice, phototherapy is a common approach. Exposing the baby’s skin to specific wavelengths of light helps break down excess bilirubin and facilitate its elimination.
- Medical Interventions: In cases of severe jaundice, especially in newborns, medical interventions like exchange transfusions might be required to rapidly reduce bilirubin levels.
- Managing Underlying Conditions: Treating the root cause of jaundice is crucial. Hepatitis, liver infections, and other liver-related issues might require specific medications or interventions.
- Surgery: If the jaundice is obstructive, such as due to gallstones or tumours, surgical procedures might be necessary to remove the obstruction.
- Lifestyle Changes: For jaundice caused by liver damage due to alcohol consumption or other factors, lifestyle changes such as quitting alcohol and adopting a healthy diet can contribute to recovery.
Prevention and Precautions
While certain causes of jaundice are unavoidable, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk:
- Maintain Hygiene: Practising good hygiene can prevent infections that might lead to hepatitis, a common cause of jaundice.
- Vaccination: Ensuring proper vaccination against hepatitis viruses can significantly reduce the risk of developing hepatitis-related jaundice.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Avoid excessive alcohol consumption and maintain a balanced diet to support overall liver health.
- Prompt Medical Attention: Any persistent symptoms of jaundice, such as yellowing of the skin or eyes, should prompt a visit to a healthcare professional for proper evaluation.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is provided by the expert and is for informational purposes only. If you notice any symptoms, visit your expert immediately.
اكتشاف المزيد من ينبوع المعرفة
اشترك للحصول على أحدث التدوينات المرسلة إلى بريدك الإلكتروني.
